The B cell-stimulating molecules, BAFF (B cell activating factor, also known as BLyS; TALL-1; CD257 or TNFSF13B) and APRIL (a proliferation-inducing ligand, also known as CD256 or TNFSF13), are critical factors in the maintenance of the B cell pool and humoral immunity (1, 2).
APRIL is a secreted protein that binds to the transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI), B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG). APRIL can interact with carbohydrate side chains of proteoglycans that may trigger cross-linking (3).
BAFF is a transmembr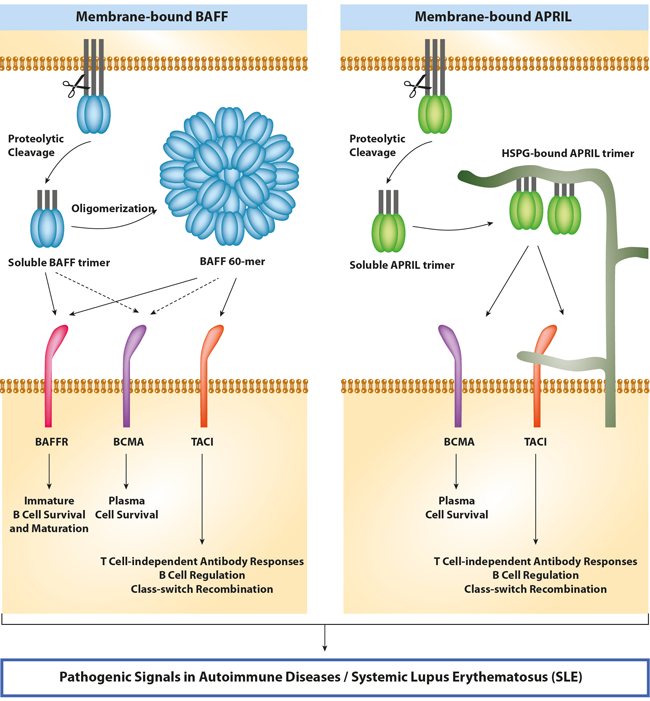 ane protein which is proteolytically processed by furin to be released as a soluble cytokine (2). Soluble BAFF exists either as trimers (BAFF 3-mer) or as an ordered assembly of 20 trimers (BAFF 60-mer) (4). BAFF 3-mer and BAFF 60-mer both signal through BAFF-R, only TACI (and BCMA) respond to BAFF 60-mer and not to BAFF 3-mer (4). Similar observations are true with APRIL, which needs to be cross-linked in order to activate TACI (4).
ane protein which is proteolytically processed by furin to be released as a soluble cytokine (2). Soluble BAFF exists either as trimers (BAFF 3-mer) or as an ordered assembly of 20 trimers (BAFF 60-mer) (4). BAFF 3-mer and BAFF 60-mer both signal through BAFF-R, only TACI (and BCMA) respond to BAFF 60-mer and not to BAFF 3-mer (4). Similar observations are true with APRIL, which needs to be cross-linked in order to activate TACI (4).
APRIL maintains B cell homeostasis by acting at a later stage, modulating the function and survival of antigen-experienced B cells. BAFF is a key survival factor for peripheral B cells and together with IL-6 plasma cell differentiation (2). APRIL (as well as BAFF) stimulates class-switch recombination (CSR), hence contributing to shaping humoral effector mechanisms. With regards to humoral memory, APRIL is involved in the establishment and survival of the long-lived plasma cell (LLPC) pool in the bone marrow (BM) (5). Besides its major role in B cell biology, BAFF co-stimulates activated T cells.
APRIL is expressed by a number of myeloid-derived cell types including BM granulocytes, megakaryocytes, eosinophils, osteoclasts, and by dendritic cells following exposure to IFN-α, IFN-γ or CD40L. APRIL expression is induced during hematopoiesis in the bone marrow. APRIL expression is not limited to cells of myeloid origin but can be found in epithelial cells of the gut, tonsil, breast and skin. Finally, APRIL is expressed in tumour cell lines and human cancer cells of the colon, thyroid and lymphoid origin (1).
APRIL confers atheroprotection by binding to heparan sulfate chains of heparan-sulfate proteoglycan 2 (HSPG2), which limits the retention of low-density lipoproteins, accumulation of macrophages and formation of necrotic cores. In this study, they use AdipoGen’s specific anti-APRIL (mouse) antibody (Apry-1-1) that promotes the binding of APRIL to HSPGs to reduce experimental atherosclerosis. They also observed that serum levels of a specific form of human APRIL that binds to HSPGs (termed non-canonical APRIL) are associated with long-term cardiovascular mortality in patients with atherosclerosis (13).
BAFF is mainly produced by innate immune cells such as neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, follicular dendritic cells, T cells, activated B cells, some malignant B cells, but non-lymphoid cells like astrocytes, synoviocytes and epithelial cells can also produce BAFF.
BAFF and APRIL are implicated in several human autoimmune diseases with autoreactive B cell involvement, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (6), Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) (7), IgA nephropathy (IgAN) (8), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (9). APRIL might also function in enhancing the proliferation of some tumour cells, especially B cell malignancies (10, 11). BAFF levels are also increased in some lymphoid cancers (12).
A recent study in Cell Reports using AdipoGen’s blocking antibodies anti-APRIL (mouse) antibody (Apry-1-1) and anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (blocking) (Sandy-2) shows that the BAFF/APRIL axis is activated in inflammation-induced preterm birth (PTB). Macrophages produce BAFF at the maternal-fetal interface and BAFF enhances inflammatory responsiveness and increases susceptibility to PTB. APRIL has the opposite function in PTB decreasing inflammation. Therefore, the new roles of BAFF or APRIL in parturition open new therapeutic possibilities for mitigating the risk of inflammation-induced PTB (14).
Literature References:
-
Targeting BAFF and APRIL in systemic lupus erythematosus and other antibody-associated diseases: E. Samy, et al.; Int. Rev. Immunol. 36, 3 (2017)
-
Cracking the BAFF code: F. Mackay & P. Schneider; Nat. Rev. Immunol. 9, 491 (2009)
-
Identification of proteoglycans as the APRIL-specific binding partners: K. Ingold, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 201, 1375 (2005)
-
TACI, unlike BAFF-R, is solely activated by oligomeric BAFF and APRIL to support survival of activated B cells and plasmablasts: C. Bossen, et al.; Blood 111, 1004 (2009)
-
Factors of the bone marrow microniche that support human plasma cell survival and immunoglobulin secretion: D.C. Nguyen, et al.; Nat. Commun. 12, 3698 (2018)
-
Raised serum APRIL levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: T. Koyama, et al.; Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64, 1065 (2005)
-
The expression of APRIL in Sjogren’s syndrome: Aberrant expression of APRIL in the salivary gland: J.L. Vosters, et al.; Rheumatology (Oxford) 51, 1557 (2012)
-
Increased APRIL Expression Induces IgA1 Aberrant Glycosylation in IgA Nephropathy: Y.L. Zhai, et al.; Medicine (Baltimore) 95, e3099 (2016)
-
The BAFF/APRIL system: an important player in systemic rheumatic diseases: F. Mackay, et al.; Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 8, 243 (2005)
-
APRIL, a New Ligand of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Family, Stimulates Tumor Cell Growth: M. Hahne, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 188, 1185 (1998)
-
In situ detection of APRIL-rich niches for plasma-cell survival and their contribution to B-cell lymphoma development: M. Burjanadze, et al.; Histol. Histopathol. 24, 1061 (2009)
-
Serum BAFF predicts prognosis better than APRIL in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with rituximab plus CHOP chemotherapy: S.J. Kim, et al.; Eur. J. Haematol. 81, 177 (2008)
-
APRIL limits atherosclerosis by binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans: D. Tsiantoulas, et al.; Nature 597, 92 (2021)
-
BAFF and APRIL counterregulate susceptibility to inflammation-induced preterm birth: R.J. Doll, et al.; Cell Reports 42, 112352 (2023)
Most Comprehensive & Unique APRIL/BAFF Reagents for Autoimmune Disease Research
NEW APRIL (human) ELISA Kit – The BEST on the Market
The APRIL (human) ELISA Kit (Prod. No. AG-45B-0012) is a sandwich ELISA for specific quantitative determination of human APRIL in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. This ELISA Kit shows both high specificity and high sensitivity, which is a clear advantage compared to other APRIL (human) ELISA Kits from key competitors, such as eBioscience or Biolegend.
Specificity:
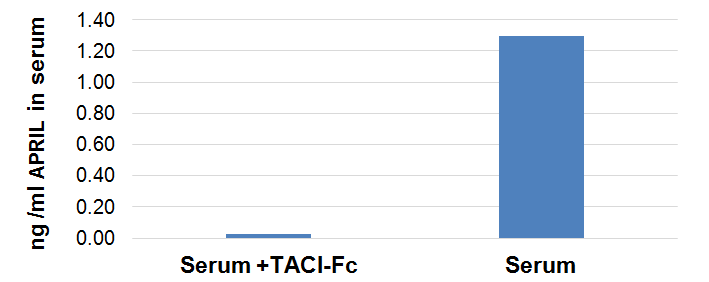 Serum from a healthy patient is left untreated or treated with 1µg/ml of the APRIL receptor, TACI (human): Fc (human) (Prod. No. AG-40B-0079). APRIL levels were measured using the APRIL (human) ELISA Kit (Prod. No. AG-45B-0012).
Serum from a healthy patient is left untreated or treated with 1µg/ml of the APRIL receptor, TACI (human): Fc (human) (Prod. No. AG-40B-0079). APRIL levels were measured using the APRIL (human) ELISA Kit (Prod. No. AG-45B-0012).
BAFF, Soluble (human) ELISA Kit (hypersensitive) – The RELIABLE Assay
The BAFF, Soluble (human) ELISA Kit (Prod. No. AG-45B-0001) is a sandwich ELISA for specific quantitative determination of human BAFF in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. This ELISA Kit does not cross-react with mouse BAFF and has been chosen by several CROs for its high specificity and high sensitivity.
Specificity:
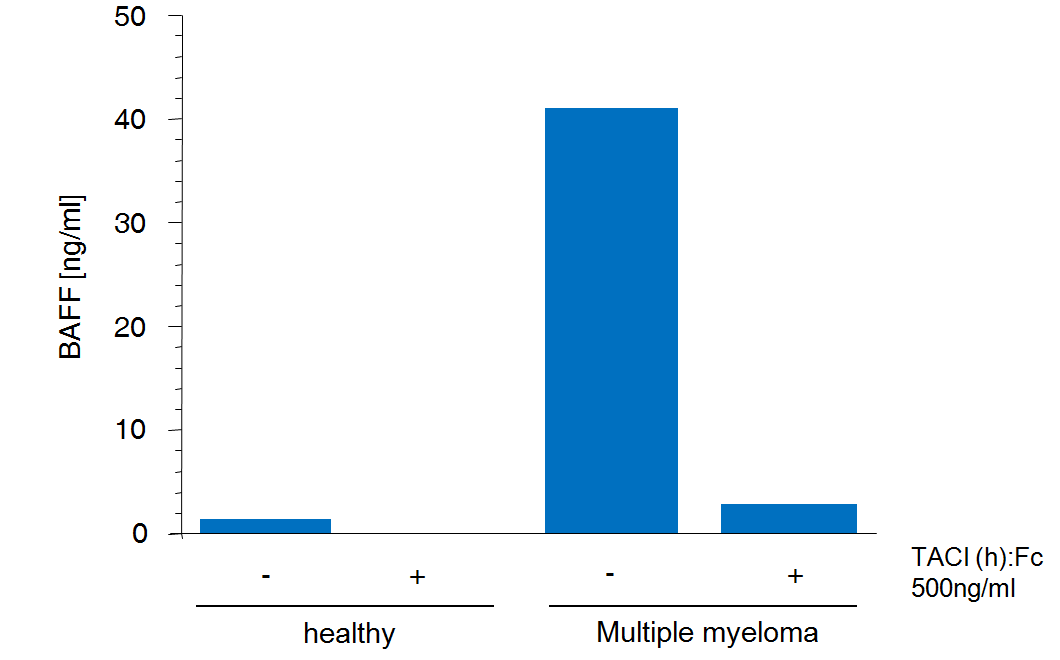 Serum from a healthy patient or patient with multiple sclerosis is left untreated or treated with 0.5 μg/ml of a BAFF receptor, TACI (human): Fc (human) (AG-40B-0079). BAFF levels are measured using the BAFF, Soluble (human) ELISA Kit (hypersensitive) (AG-45B-0001).
Serum from a healthy patient or patient with multiple sclerosis is left untreated or treated with 0.5 μg/ml of a BAFF receptor, TACI (human): Fc (human) (AG-40B-0079). BAFF levels are measured using the BAFF, Soluble (human) ELISA Kit (hypersensitive) (AG-45B-0001).
NEW APRIL/BAFF (human) Tandem ELISA Kit
AdipoGen Life Sciences launched a highly sensitive APRIL/BAFF (human) Tandem ELISA Kit (Prod. No. AG-45B-4501), consisting of one each of our specific worry-free APRIL and BAFF ELISA Kits (AG-45B-0001 and AG-45B-0012, respectively). Inquire for preferable BULK prices for extensive studies.
UNIQUE & POTENT anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (blocking) (Sandy-2)
AdipoGen Life Sciences’ anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (blocking) (Sandy-2) (Prod. No. AG-20B-0063) is a monoclonal antibody that recognizes mouse BAFF and works specifically in IP and Functional Application. The antibody inhibits mouse BAFF binding to BAFF-R and TACI. It is highly potent in blocking mouse BAFF in vivo and induces B cell depletion and generates a phenotype similar to that observed in BAFF-/- mice. The antibody is available with or without preservatives.
Specificity:
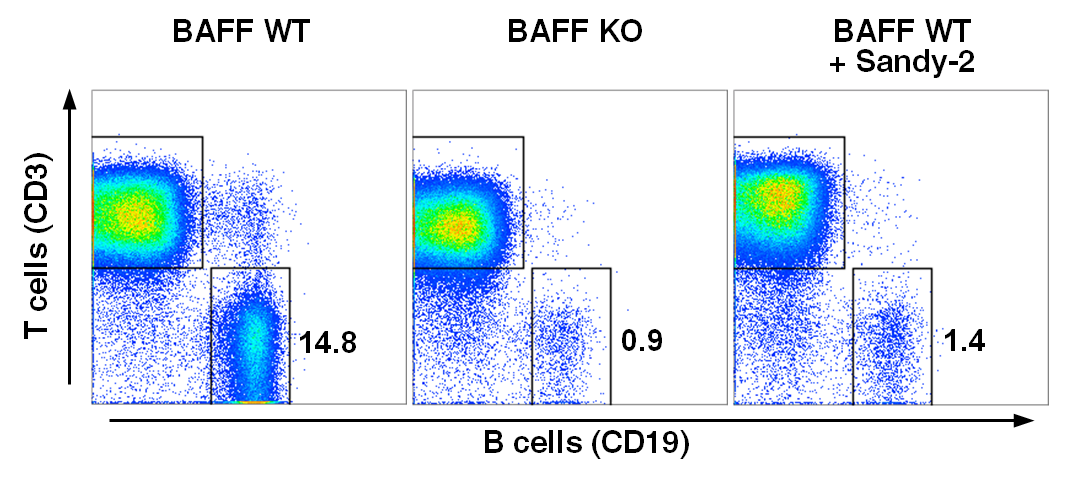 Figure: anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (Sandy-2) (Prod. No. AG-20B-0063) blocks the action of endogenous BAFF in vivo.
Figure: anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (Sandy-2) (Prod. No. AG-20B-0063) blocks the action of endogenous BAFF in vivo.
Method: Wild type C57BL/6 mice were treated at day 0 (single administration) with monoclonal antibody anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (Sandy-2) (at 2mg/kg). Lymph nodes were prepared at week 2 and analyzed by FACS for the presence of T (CD3) and B (CD19) cells. Untreated BAFF WT and KO mice were analyzed in parallel.
UNIQUE & POTENT anti-APRIL (mouse), mAb (rec.) (blocking) (Apry-1-1)
AdipoGen Life Sciences’ anti-APRIL (mouse), mAb (rec.) (blocking) (Apry-1-1) (Prod. No. AG-27B-0001) is a recombinant monoclonal antibody that recognizes mouse APRIL and works specifically in IP and Functional Application. The antibody inhibits mouse APRIL binding to BCMA and TACI. It is highly potent in blocking mouse APRIL in vitro and in vivo. The antibody is available with or without preservatives.
Specificity:
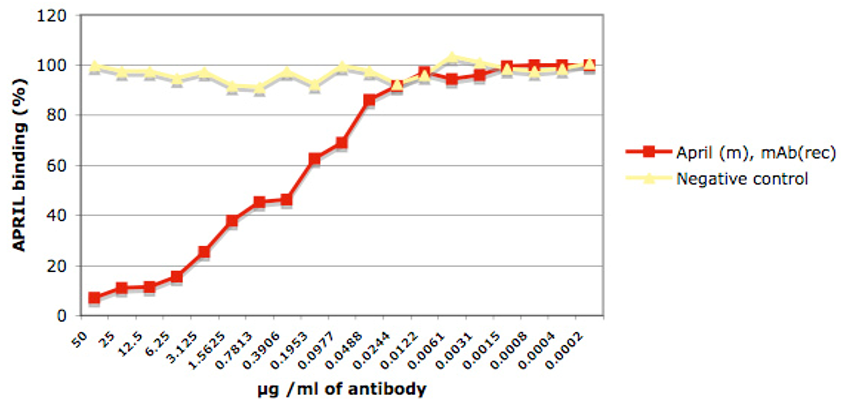 Figure: Binding of APRIL (mouse) to BCMA is inhibited by anti-APRIL (mouse), mAb (rec.) (blocking) (APRY-1-1) (Prod. No. AG-27B-0001).
Figure: Binding of APRIL (mouse) to BCMA is inhibited by anti-APRIL (mouse), mAb (rec.) (blocking) (APRY-1-1) (Prod. No. AG-27B-0001).
Method: BCMA:Fc was coated on an ELISA plate at 1μg/ml. anti-APRIL (mouse) mAb (rec.) (blocking) (APRY-1-1) or an unrelated mAb (recombinant) (Negative control) were added (starting at 50μg/ml with a twofold serial dilution) together with 0.1μg/ml of MultimericAPRIL (mouse). After incubation for 1h at RT, the MultimericAPRIL (mouse) binding was detected using an anti-FLAG® antibody (HRP). The percentage of binding is shown.
NEW & UNIQUE anti-APRIL (mouse), mAb (blocking) (Centotto-1) (preservative free)
AdipoGen Life Sciences’ anti-APRIL (mouse), mAb (blocking) (Centotto-1) (preservative free) (Prod. No. AG-20B-0083PF) is a monoclonal antibody that recognizes mouse APRIL and works specifically in IP and Functional Application. The antibody depletes mouse APRIL in vivo and is available without preservatives.
UNIQUE Highly Active Proteins – Developed & Manufactured at AdipoGen Life Sciences
AdipoGen Life Sciences, with its deep roots in TNF Superfamily research, provides a unique panel of highly active and multimeric APRIL and BAFF recombinant proteins. The validated high quality research tools are used and published by the experts in BAFF and APRIL research on a daily basis.
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
|---|---|---|
| APRIL (human) (multimeric) (rec.) | AG-40B-0017 | MultimericAPRIL™ is a high activity construct in which two trimeric APRIL ligands are artificially linked via the collagen domain of ACRP30. This construct very effectively stimulates B cell proliferation. This protein binds to human and mouse BCMA and TACI and to proteoglycans. |
| APRIL (human) (H98) (multimeric) (rec.) | AG-40B-0088 | MultimericAPRIL™ is a high activity construct in which two trimeric APRIL ligands are artificially linked via the collagen domain of ACRP30. This construct very effectively stimulates B cell proliferation. This protein binds to human and mouse BCMA and TACI. Does not bind to proteoglycans. |
| APRIL (mouse) (multimeric) (rec.) | AG-40B-0089 | MultimericAPRIL™ is a high activity construct in which two trimeric APRIL ligands are artificially linked via the collagen domain of ACRP30. This construct very effectively stimulates B cell proliferation. This protein binds to human and mouse BCMA and TACI and to proteoglycans. |
| APRIL (mouse) (H98) (multimeric) (rec.) | AG-40B-0035 | MultimericAPRIL™ is a high activity construct in which two trimeric APRIL ligands are artificially linked via the collagen domain of ACRP30. This construct very effectively stimulates B cell proliferation. This protein binds to human and mouse BCMA and TACI. Does not bind to proteoglycans. |
| BAFF, Soluble (human) (60-mer) (rec.) (highly active) | AG-40B-0112 | Binds to human and mouse BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA. Increases B cell survival/proliferation. Increases CD21/CD23 expression on B cells in vivo. Activates BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA receptors. |
| BAFF (aa134-285), Soluble (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0016 | Binds to human and mouse BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA. |
| Fc (human):BAFF (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0120 | Binds to human and mouse BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA. Rescues the production of mature follicular and marginal zone B cells in vitro and in vivo. |
| BAFF, Soluble (mouse) (rec.) | AG-40B-0022 | Binds to human and mouse BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA. |
| BAFF-R (human):Fc (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0027 | Binds to human and mouse BAFF. Inhibits BAFF activity. |
| BCMA (human):Fc (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0080 | Binds mouse and human BAFF and APRIL. Blocks the binding of BAFF and APRIL to their receptors BCMA and TACI, inhibiting BAFF- and APRIL-mediated B cell activation. |
| BCMA (mouse):Fc (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0076 | Binds mouse and human BAFF and APRIL. Blocks the binding of mouse BAFF and human APRIL to their receptors BCMA and TACI. |
| TACI (human):Fc (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0079 | Binds to human and mouse BAFF and APRIL. Inhibits BAFF and APRIL activity. |
VALIDATED Antibodies for BAFF and APRIL Research
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
|---|---|---|
| NEW anti-APRIL (human), mAb (rec.) (blocking) (Mahya-1) (preservative free) | AG-20B-0078PF | Recognizes human APRIL. Does not recognize mouse APRIL or mouse and human BAFF. Inhibits the binding of human APRIL to BCMA and TACI. |
| UNIQUE anti-APRIL (mouse), mAb (rec.) (blocking) (Apry-1-1) | AG-27B-0001 | Recognizes mouse APRIL and is used in IP und Functional application. Does not recognize mouse BAFF. Inhibits the binding of mouse APRIL to BCMA and TACI in vitro and in vivo. Promotes the binding of APRIL to HSPGs and confers atheroprotection. |
| anti-APRIL (mouse), mAb (rec.) (blocking) (Apry-1-3) | AG-27B-0017 | Recognizes mouse APRIL. Does not recognize mouse BAFF. Inhibits the binding of mouse APRIL to BCMA and TACI. |
| NEW anti-APRIL (mouse), mAb (blocking) (Centotto-1) (preservative free) | AG-20B-0083PF | Recognizes mouse APRIL and is used in IP und Functional application. The antibody depletes mouse APRIL in vivo |
| BAFF, Soluble (human) Matched Pair Detection Set | AG-46B-0001 | Detects human BAFF in plasma, serum and cell culture supernatant with a sensitivity of 16pg/ml. Does not detect mouse BAFF. |
| anti-BAFF (human), mAb (blocking) (4.62) | AG-20B-0017 | Recognizes human BAFF. Inhibits human BAFF binding and is used in IP application. |
| anti-BAFF (human), mAb (2.81) | AG-20B-0018 | Recognizes human BAFF and is used in IP application. |
| anti-BAFF (human), mAb (1-35-1) | AG-20B-0037 | Recognizes human BAFF and is used in FACS application. |
| anti-BAFF (human), mAb (ANC2H3) | ANC-266-020 | Recognizes human BAFF. Inhibits human BAFF binding and is used in FACS application. |
| UNIQUE anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (blocking) (Sandy-2) | AG-20B-0063 | Recognizes mouse BAFF and is used in IP and Functional application. Injection of the anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (Sandy-2) in mice creates a BAFF KO phenotype within 2 weeks, that can be maintained as long as necessary (> 6 months) by further injections of Sandy-2 every 2 weeks. |
| anti-BAFF-R (human), mAb (HuBR9.1) | AG-20B-0016 | Recognizes human BAFF-R. The Standard for FACS application. |
| anti-BAFF-R (mouse), mAb (9B9) | AG-20B-0034 | Recognizes mouse BAFF-R. Used for depletion of B cells in vivo and in FACS application. |
| anti-BAFF-R (human), mAb (ANC268.2/6E6) | ANC-275-020 | Recognizes human BAFF-R. Used for FACS application. |
| anti-BCMA (human), mAb (ANC3B1) | ANC-269-020 | Recognizes human BCMA. Used for FACS application. |
| anti-TACI (mouse), mAb (1A-10) | AG-20B-0035 | Recognizes mouse TACI. The Standard for FACS application. |
Other Reagents for BAFF and APRIL Research
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
|---|---|---|
| anti-LTβR (human), mAb (ANCLTR2/9E2) | ANC-267-020 | Recognizes human LTβR. Used in FACS application. |
| anti-LTβR (mouse), mAb (4H8 WH2) | AG-20B-0008 | Recognizes mouse LTβR. Agonistic antibody inducing BAFF, chemokines and integrins in vitro and in vivo and used in FACS application. |
| anti-LTβR (mouse), mAb (3C8) | AG-20B-0041 | Recognizes mouse LTβR. Agonistic antibody inducing BAFF, chemokines and integrins in vitro and in vivo and used in FACS application. |
| LIGHT, Soluble (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0009 | Binds to human and mouse LTβR and human HVEM and DcR3. |
| IL-35 (human):Fc (human) (rec.) | CHI-HF-21035 | Bioactive in a cell proliferation assay using anti-CD3 activated human peripheral mononuclear cells. |
| IL-35 (mouse):Fc (human) (rec.) | CHI-MF-11135 | Bioactive in a cell proliferation assay of Con A activated mouse splenocytes and in in vivo studies. |
Originally posted by Adipogen on: adipogen.com/autoimmune-diseases-biomarker
Caltag Medsystems is the distributor of Adipogen products in the UK and Ireland. If you have any questions about these products, please contact us.
