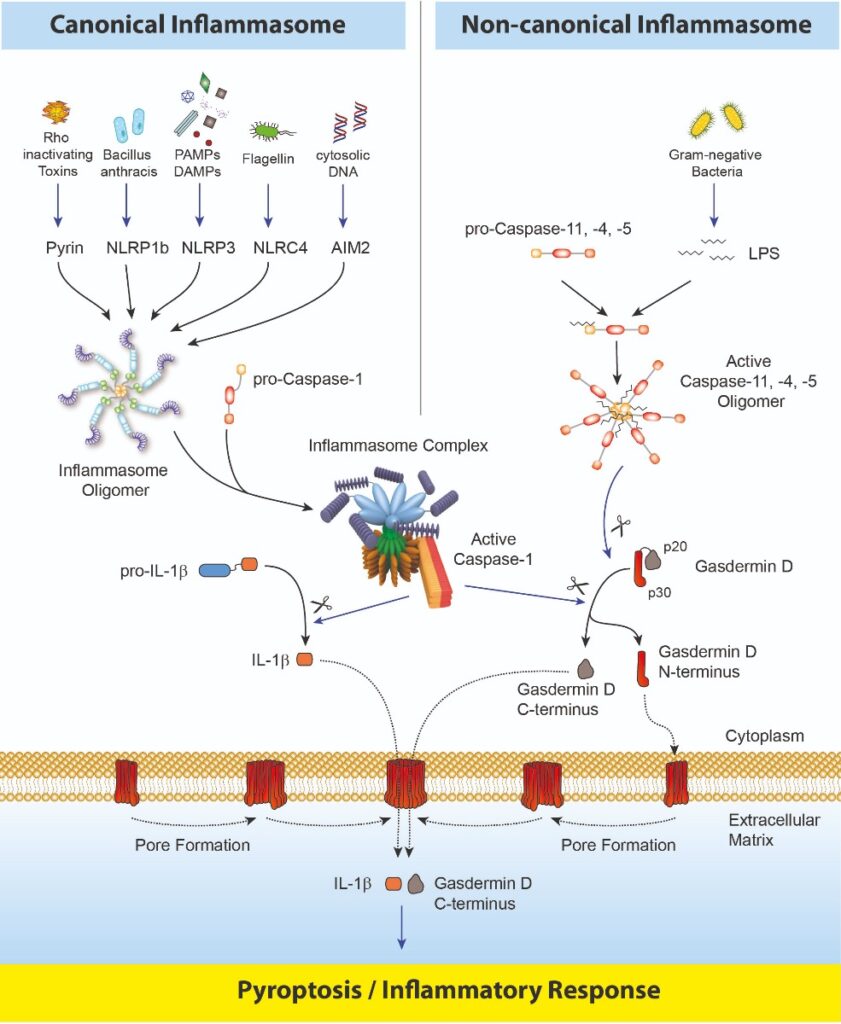
Inflammasomes are multimeric protein complexes that comprise a sensor (e.g. NLRP3), an adaptor (ASC/Pycard) and a protease (pro-caspase-1) (1). An inflammasome assembles in response to a diverse range of pathogen-associated or danger-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs or DAMPs), or perturbations in cytoplasmic homeostasis (term ‘homeostasis-altering molecular processes’ (HAMPs)) (2). The inflammasome platform leads to the activation of caspase-1, which further induces the maturation of interleukin-1β and -18 (IL-1β and IL-18) through proteolytic cleavage of pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18. Activated caspase-1, and also the recently characterised caspase-11 non-canonical inflammasome pathway, cleave the newly discovered intracellular protein Gasdermin D (3, 4). The Gasdermin family members contain N-terminal domains that are capable of forming membrane pores, whereas the C-terminal domains of Gasdermins function as inhibitors of such cytolysis through intramolecular domain association. Caspase-1 or -11 cleavage of Gasdermin D is required for regulation of Pyroptosis: upon caspase-1/11 cleavage of the Gasdermin N- and C-domain linker, the cleaved N-terminal fragment of Gasdermin D oligomerises and forms pores on the host cell membrane (5), leading to a cell death called pyroptosis and further activation of inflammasomes by triggering K+ efflux (6). Gasdermin D forming pores regulate the non-conventional secretion of cytokines such as IL-1β, in response to cytosolic LPS and other activators of the inflammasome (7). Neutrophil extrusion of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and concomitant cell death (NETosis), a particular neutrophil defence against pathogens, are dependent on Gasdermin D cleavage by caspase-11 (8). Gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis is regulated at the level of lipid peroxidation (9) and seems to be a key effector in LPS-induced lethal sepsis (10).
Caspase-8, an upstream activator of caspase-3, controls apoptotic cell death and prevents RIPK3–MLKL-dependent necroptosis. Caspase-8, activated by the Yersinia effector protein YopJ, also triggers Gasdermin D processing and cell death with different Yersinia species (11).
After the formation of the pore at the cellular membrane by the Gasdermin D N-terminal fragment, the role and fate of the C-terminus fragment of Gasdermin D is still unclear. Using the Gasdermin D (mouse) ELISA Kit (Prod. No. AG-45B-0011), which detects the C-terminal part of Gasdermin D (as well as the full-length protein), a signal is detected in the supernatant of cells dying by pyroptosis, suggesting that the C-terminal fragment is released from cells, either by chance due to the presence of a pore or for a specific task not yet clear.
Literature References:
- The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta: F. Martinon, et al.; Mol. Cell 10, 417 (2002)
- Homeostasis-altering molecular processes as mechanisms of inflammasome activation: A. Liston & S.L. Masters; Nat. Rev. Immunol. 17, 208 (2017)
- Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling: N. Kayagaki, et al.; Nature 526, 666 (2015)
- Mechanisms of Gasdermin Family Members in Inflammasome Signaling and Cell Death: S. Feng, et al.; J. Mol. Biol. 430, 3068 (2018)
- Inflammasome-activated gasdermin D causes pyroptosis by forming membrane pores: X. Liu, et al.; Nature 535, 153 (2016)
- Gasdermin D Restrains Type I Interferon Response to Cytosolic DNA by Disrupting Ionic Homeostasis: I. Banerjee, et al.; Immunity 49, 413 (2018)
- The Pore-Forming Protein Gasdermin D Regulates Interleukin-1 Secretion from Living Macrophages: C.L. Evavold, et al.; Immunity 48, 35 (2018)
- Noncanonical inflammasome signaling elicits gasdermin D-dependent neutrophil extracellular traps: K.W. Chen, et al.; Sci. Immunol. 3, 26 (2018)
- Lipid Peroxidation Drives Gasdermin D-mediated Pyroptosis in Lethal Polymicrobial Sepsis: R. Kang, et al.; Cell Host Microbe 24, 97 (2018)
- Chemical disruption of the pyroptotic pore-forming protein gasdermin D inhibits inflammatory cell death and sepsis: J.K. Rathkey, et al.; Sci. Immunol. 3, 26 (2018)
- Pathogen blockade of TAK1 triggers caspase-8-dependent cleavage of gasdermin D and cell death: P. Orning, et al.; Science (Epub ahead of print) 26 (2018)
New Reagents for Gasdermin Research
NEW Gasdermin D (mouse) ELISA Kit
The Gasdermin D (mouse) ELISA Kit (Prod. No. AG-45B-0011) is a sandwich ELISA for the quantitative determination of mouse Gasdermin D in cell culture supernatants and in cell extracts. This ELISA is specific for the measurement of natural and recombinant mouse Gasdermin D (full-length and C-terminus cleaved fragment). It does not detect human Gasdermin D.
Specificity:
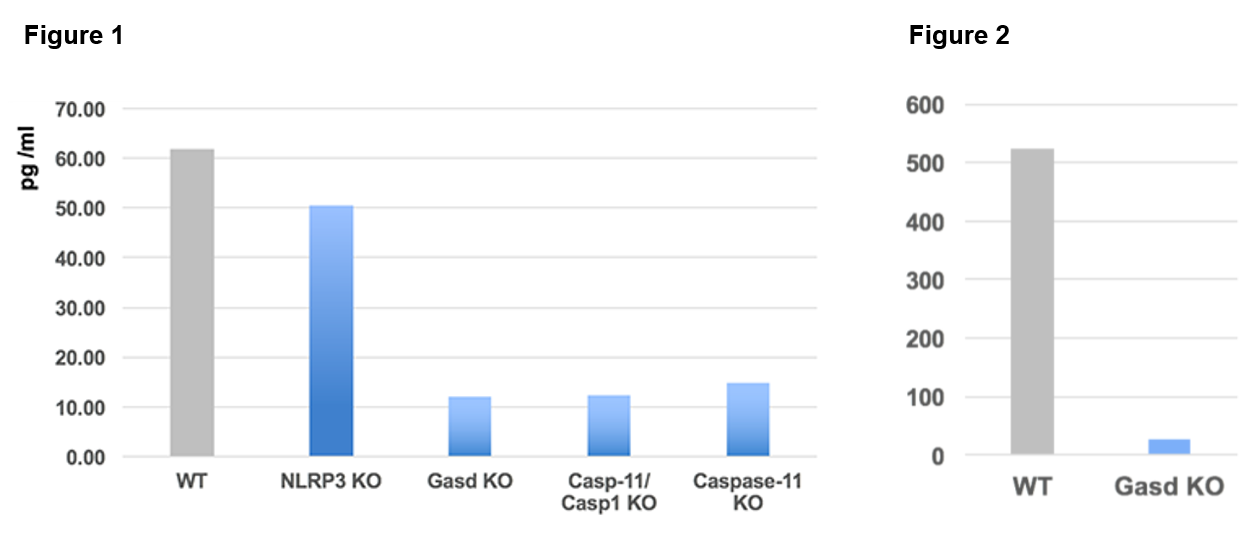
Gasdermin D is tested from supernatants of Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages cells (BMDMs) transfected with LPS from different knockout mice strains (see Figure 1). Only the supernatants from WT and NLRP3-/- strains contain the protein Gasdermin D. Gasdermin D is also tested from cell extracts (lysed with a Triton X-100 buffer) of Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages cells from WT and Gasdermin D knockout mice strains (see Figure 2).
NEW Gasdermin E (human) ELISA Kit
Gasdermin E (GSDME), also called DFNA5, is a member of the gasdermin family. Recent studies found that GSDME features a caspase-3 cleavage motif in its linker region. Similar to GSDMD, cleavage of GSDME by caspases-3/-7 liberates the N-terminal pyroptosis-inducing domain (GSDMENT) from its autoinhibitory C-terminal regulatory domain to trigger membrane pores and pyroptosis. Mutations in GSDME in humans are associated with the development of heritable, nonsyndromal deafness. Abnormalities in pyroptotic cell deaths are associated with a range of human diseases including infections, autoinflammatory disease, neurodegenerative disease and cancer. The Gasdermin E (human) ELISA Kit (AG-45B-0024) detects the C-terminal domain of human Gasdermin E as well as the full-length protein. Upon cleavage of Gasdermin E and pore formation, the C-terminus fragment should be released in the extracellular space and is found in serum/plasma. The role of the C-terminus fragment of Gasdermin protein family is unclear.
NEW anti-Gasdermin D (mouse), pAb (IN110)
AdipoGen Life Sciences’ anti-Gasdermin D (mouse), pAb (IN110) (Prod. No. AG-25B-0036) is a polyclonal antibody immunised with the recombinant C-terminus domain of mouse Gasdermin D. The antibody recognises full-length and the cleaved C-terminus of mouse Gasdermin D, does not cross-react with human Gasdermin D and works specifically in Western Blot application to detect the cleaved C-terminal Gasdermin D.
Specificity:
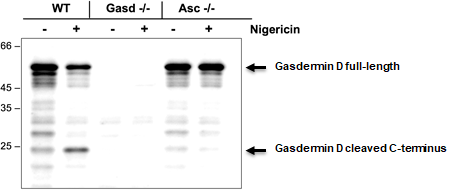
Figure: Mouse Gasdermin D (full-length and cleaved p22 fragments) are detected by immunoblotting using anti-Gasdermin D (mouse), pAb (IN110) (Prod. No. AG-25B-0036).
Method: Gasdermin D is analysed by Western blot in cell extracts of bone marrow-derived macrophage cells (BMDMs) (WT, Gasdermin -/- or Asc -/-) treated with LPS (50ng/ml; Prod. No. AG-CU1-0001) for 3h and +/- Nigericin (5μM for 2.5h, Prod. No. AG-CN2-0020). Cell extracts are separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, transferred to nitrocellulose and incubated with anti-Gasdermin D (mouse), pAb (IN110) (0.5µg/ml). After the addition of an anti-guinea pig secondary antibody coupled to HRP (1/5000), proteins are visualised by a chemiluminescence detection system.
Picture courtesy of Prof. Olaf Gross, University Medical Center Freiburg, Germany.
The Standard Inflammasome Research Antibodies – Validated Reliable Antibodies used by experts
AdipoGen Life Sciences is the “No. 1” manufacturer and supplier of inflammasome signalling research reagents. The validated high-quality inflammasome research tools are used and published by experts in inflammasome research on a daily basis.
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
|---|---|---|
| anti-Caspase-1 (p20) (mouse), mAb (Casper-1) | AG-20B-0042 | Recognizes endogenous full-length and activated (p20 fragment) mouse caspase-1. |
| anti-Caspase-1 (p10) (mouse), mAb (Casper-2) | AG-20B-0044 | Recognizes endogenous full-length and activated (p10 fragment) mouse caspase-1. |
| anti-Caspase-1 (p20) (human), mAb (Bally-1) | AG-20B-0048 | Recognizes endogenous full-length and activated (p20 fragment) human caspase-1. |
| anti-NLRP3/NALP3, mAb (Cryo-2) | AG-20B-0014 | Recognizes mouse and human NLRP3/NALP3. Over 1000 Citations! |
| anti-Asc, pAb (AL177) | AG-25B-0006 | Recognizes human and mouse Asc. |
| anti-IL-1α (p18) (mouse), mAb (Teo-1) | AG-20B-0064 | Recognizes full-length and cleaved p18 fragment of mouse IL-1α. |
| anti-Caspase-8 (human), mAb (C15) | AG-20B-0057 | Recognizes the p18 subunit of human caspase-8. |
| anti-Caspase-8 (mouse), mAb (1G12) | AG-20T-0137 | Recognizes full-length and the p18 cleaved fragment of mouse caspase-8. |
| anti-Caspase-8 (mouse), mAb (3B10) | AG-20T-0138 | Recognizes full-length and the p18 cleaved fragment of mouse caspase-8. |
| anti-Caspase-4 /11 (p20), mAb (Flamy-1) | AG-20B-0060 | Recognizes endogenous full-length protein and activated (p20) fragment of mouse and human caspase-4/11. Does not detect human Caspase-5. |
NEW IL-1β (human) ELISA Kit – HIGH SENSITIVITY
The IL-1β (human) ELISA Kit (Prod. No. AG-45B-0021) is a sandwich ELISA for the quantitative determination of human IL-1β in cell culture supernatants, serum and plasma samples. This ELISA assay is specific and highly sensitive (0.7pg/ml) for the measurement of natural and recombinant human IL-1β.
Active IL-1β has known roles in initiating and propagating sterile inflammation, including macrophage recruitment, activation of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) and modulating chemokine expression. IL-1β, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes play important roles in several diseases such as sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, atherosclerosis, neuronal injuries, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, cerebral ischemic cell death, multiple sclerosis and Down syndrome. Some human hereditary or acquired diseases have been linked to elevated IL-1β such as cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS) directly linked to NLRP3 mutations.
The Key Inflammasome Activators and Inhibitors – Including New Gasdermin Inhibitor
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
|---|---|---|
| Monosodium urate (crystals) | AG-CR1-3950 | Potent NLRP3 inflammasome activator. |
| Monosodium urate (ready-to-use) | AG-CR1-3951 | Potent NLRP3 inflammasome activator. |
| Nigericin . Na | AG-CN2-0020 | Potent NLRP3 inflammasome activator. |
| N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine | AG-CN2-0489 | Acts as activator of NLRP3 inflammasome by dissociating the enzyme hexokinase from the mitochondria. |
| Necrosulfonamide NEW | AG-CR1-3705 | Binds directly to Gasdermin D and inhibits the oligomerization of the N-terminus and therefore the pore formation and pyroptosis. |
| U-73122 NEW | AG-CR1-3698 | Gasdermin D N-terminal fragment (GSDMD-N)-induced pyroptosis inhibitor. Protects against GSDMD-N cytotoxicity in macrophages or against lethal infection in mice. |
| MCC950 . Na (water soluble) | AG-CR1-3615 | Potent and selective NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor. |
| Isoliquiritigenin | AG-CN2-0459 | Inhibits NLRP3-activated Asc oligomerization. Blocks priming and activation steps. |
| BAY 11-7082 | AG-CR1-0013 | Reduces ATPase activity of the NLRP3 inflammasome. |
| (R)-3-Hydroxybutyric acid | AG-CR1-3616 | Prevent K+-efflux and consequently reduce Asc oligomerization and speck formation. |
| (S)-3-Hydroxybutyric acid | AG-CR1-3617 | Prevent K+-efflux and consequently reduce Asc oligomerization and speck formation. |
| DL-3-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium salt | CDX-H0080 | Prevent K+-efflux and consequently reduce Asc oligomerization and speck formation. |
| K777 [K11777] NEW | AG-CR1-0158 | Broad-range cathepsin inhibitor useful for inflammasome inhibition. |
Priming Step of Inflammasome Activation
The most prominent function of the NLRP3 inflammasome is the processing and activation of pro-interleukin-1β (pro-IL-1β). Yet most cells do not express pro-IL-1β and thus prior expression of pro-IL-1β is required. This can be achieved by stimulating receptors such as TLRs (e.g. through LPS), Nods, TNF-Rs (e.g. through TNF-α) or IL-1R1 (through IL-1α and IL-1β) that activate NF-κB and initiate pro-IL-1β transcription. This process is called priming. Priming also induces NF-κB-dependent transcription of NLRP3.
Originally posted by Adipogen on: adipogen.com/gasdermin-d
Caltag Medsystems is the distributor of Adipogen products in the UK and Ireland. If you have any questions about these products, please contact us.
