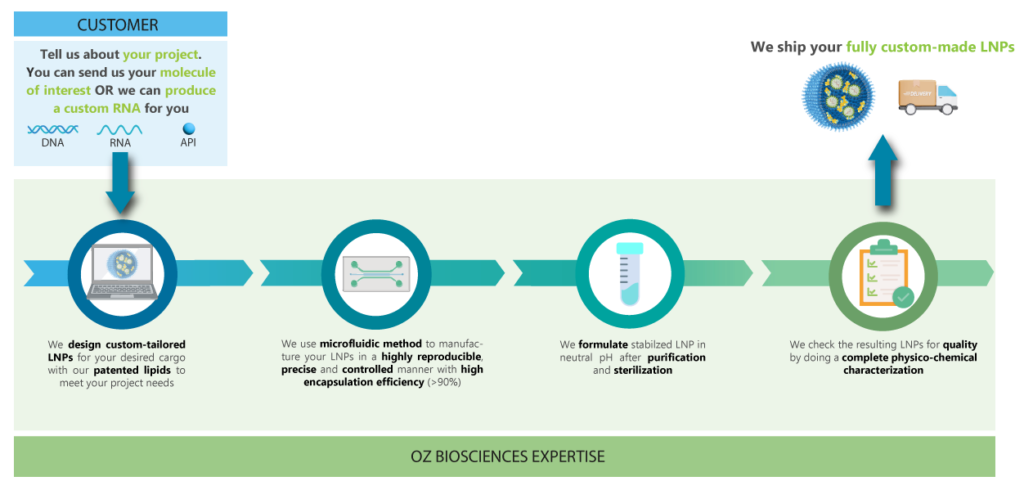
OZ Biosciences LNP Custom Service
OZ Biosciences has developed a Microfluidics Platform for the reproducible development of safe & potent drug delivery vehicles for pharmaceutical applications.
They can support every stage of your mRNA-LNP production, from mRNA synthesis to LNP formulation development, manufacturing and fill & finish.
For any RNA, DNA or API encapsulation, you can provide them with your molecule of interest and they will formulate it into LNPs.
Discover the Custom LNP Service Workflow
The OZ Biosciences team is dedicated to providing you with high-quality LNPs that meet your project needs. You can provide your own molecule of interest to encapsulate or they can make a custom mRNA for you.
OZ Biosciences Stock LNPs
Aside from their custom service, OZ Biosciences also offers ready-to-use NanOZ-LNP/mRNA products and NanOZ LNP-DIY: Lipid mix for LNP formulation for your research studies:
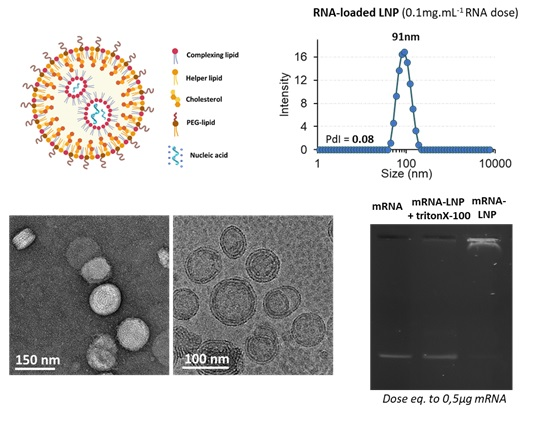
Physico-chemical characterisation of LNPs
NanOZ-LNPs are formulated through pressure-driven controlled flow microfluidics systems. Once collected and purified, NanOZ-LNPs physico-chemical properties are fully characterised in terms of size distribution, charge surface, structure integrity, encapsulation efficiency and stability.
The NanOZ-LNP/mRNA are monodisperse nanoparticles of spherical morphology with sizes usually ranging between 80-150nm and PDI<0.2. Once encapsulated, the integrity of the mRNA is verified by gel electrophoresis.
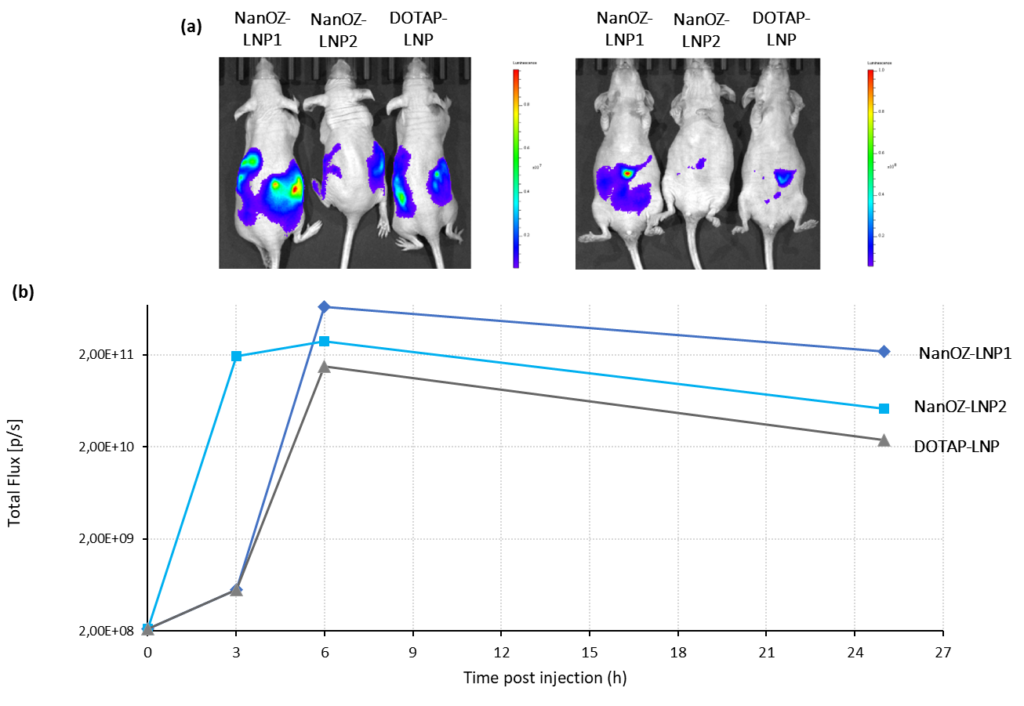
NanOZ-LNP in vivo Data
The biodistribution and transfection efficiency of NanOZ-LNP loaded with Firefly Luciferase mRNA (mRNA-Luc) was evaluated after i.p. injection of 10µg mRNA formulated in LNP in nude mice with two formulations based on proprietary ionisable lipids compared with an LNP formulation based on DOTAP cationic lipid. Bioluminescence intensity was monitored by IVIS instrument over 25h.
As observed in Figure 2, a single intra-peritoneal (i.p.) injection of Luc-LNPs enables high bioluminescence signal and luciferase expression into surrounded organs for at least 25h (Figure 4). The highest transfection efficiency was observed for the NanOZ-LNP1 formulation.
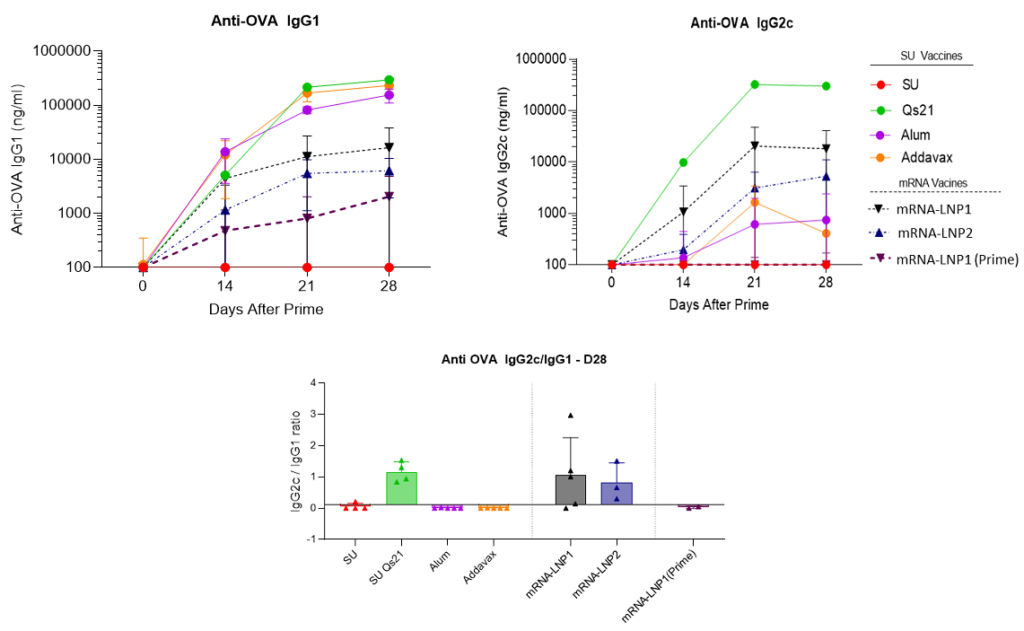
NanOZ-LNP in vivo Immunisation Results
The comparison between mRNA-based vaccines versus subunit vaccines for immune efficacy was evaluated in C57BL6J mice using the ovalbumin model. Prime boost (D0-14) immunisations were evaluated with OVA antigen delivered by mRNA-based LNPs, where two different formulations were tested corresponding to LNP1 and LNP2, or by recombinant protein (alone or adjuvanted). To characterise the immuno-phenotyping of the mice the sera were collected at D0, D14, D21 and D28 and splenocytes were collected at D28 and analysed by ELISA, Elispot and Multiplex. The mice were immunised by s.c. route with 10µg OVA subunit (SU) or 10µg mRNA doses (100µL per injection).
RNA vaccine LNP formulations are efficient at priming a strong Th1 humoral response equivalent to the best TH1 adjuvants such as QS-21 upon sub-cutaneous prime boost injection (D0-14) in C57BL6J mice. In addition, no significative signal was observed when the OVA antigen was directly administrated. It is noteworthy, the necessity of two injections (boost at D14) to obtain a long-lasting immune response.
NanOZ-LNP in vitro Evaluation
Data shows that LNP-carrying mRNA can be used for transfecting cells in vitro but with less efficiency than classic transfection reagents such as RmesFect: at least 10 times more material would be needed using LNP. Depending on the cell line (such as JurKat T cells cultivated in suspension) LNP could be an alternative to transfection reagents for genetic modification with a very high efficiency; however, the fluorescence intensity that could account for the number of delivered molecules is still below.
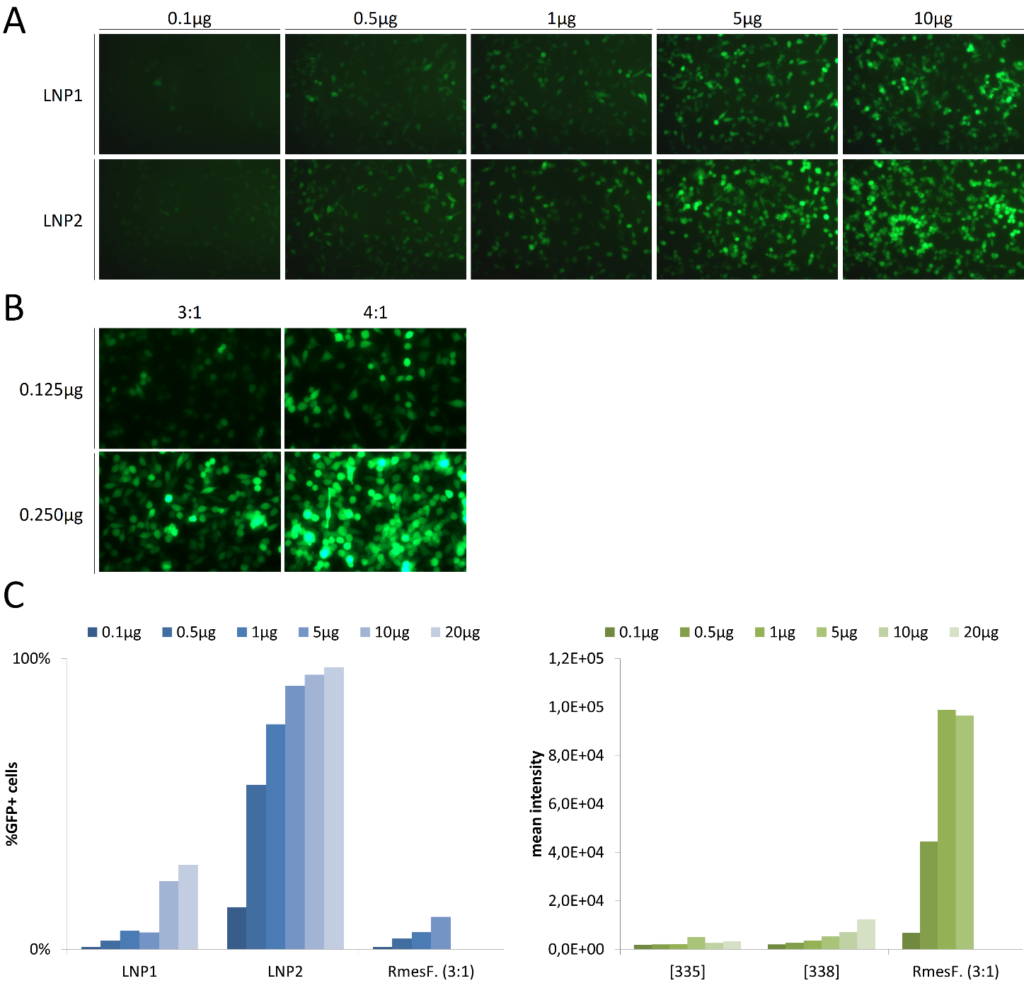
Information originally from: https://ozbiosciences.com/content/43-nanoz-lnp-lipid-nanoparticles
Caltag Medsystems is the distributor of OZ Biosciences products in the UK and Ireland. If you have any questions about these products, please contact us.
