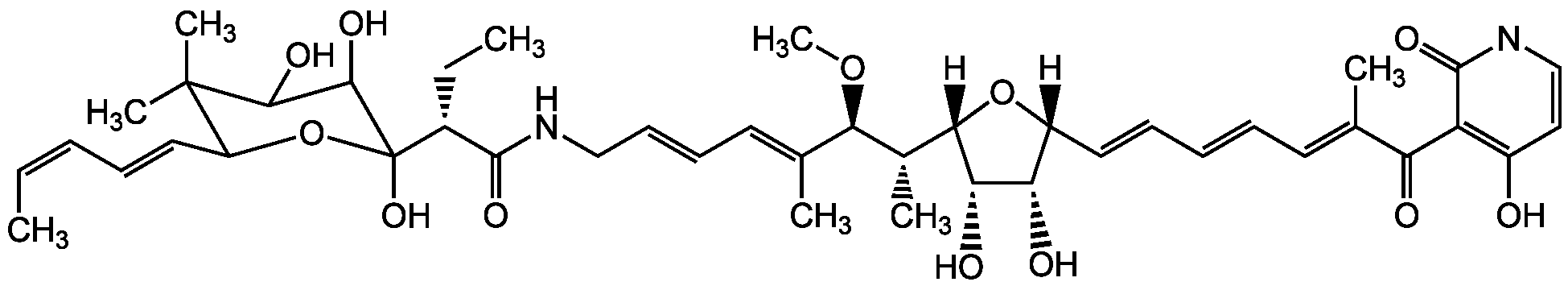
Kirromycin
Product Code:
BVT-0157
BVT-0157
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| BVT-0157-M001 | 1 mg | £205.00 |
Quantity:
| BVT-0157-M005 | 5 mg | £780.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Mocimycin; Delvomycin; MYC 8003; NSC 316094
Appearance:
Yellow powder.
CAS:
50935-71-2
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Hazards:
H315, H319, H335, EUH066
InChi:
InChI=1S/C43H60N2O12/c1-9-11-13-21-31-42(6,7)38(50)39(51)43(54,57-31)28(10-2)40(52)44-23-17-16-19-26(4)36(55-8)27(5)37-35(49)34(48)30(56-37)20-15-12-14-18-25(3)33(47)32-29(46)22-24-45-41(32)53/h9,11-22,24,27-28,30-31,34-39,48-51,54H,10,23H2,1-8H3,(H,44,52)(H2,45,46,53)/b11-9-,14-12+,17-16+,20-15+,21-13+,25-18+,26-19+/t27-,28-,30-,31+,34+,35+,36-,37+,38+,39-,43-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
HMSYAPGFKGSXAJ-PAHGNTJYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 50935-71-2. Formula: C43H60N2O12. MW: 796.9. Isolated from Streptomyces collinus. Antibiotic. Member of the elfermycin group. Antibacterial. Protein biosynthesis inhibitor. Specifically interacts with the bacterial elongation factor EF-Tu and prevents the release of EF-Tu from the bacterial ribosome after GTP hydrolysis. In the absence of ribosomes it induces EF-Tu-dependent hydrolysis of GTP. Animal growth promoter used in poultry breeding.
MDL:
MFCD00467139
Molecular Formula:
C43H60N2O12
Molecular Weight:
796.9
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Precautions:
P261, P271, P280, P312
Product Description:
Antibiotic. Member of the elfermycin group. Antibacterial. Protein biosynthesis inhibitor. Specifically interacts with the bacterial elongation factor EF-Tu and prevents the release of EF-Tu from the bacterial ribosome after GTP hydrolysis. In the absence of ribosomes it induces EF-Tu-dependent hydrolysis of GTP. Animal growth promoter used in poultry breeding.
Purity:
>96% (HPLC)
Signal Word:
Warning
SMILES:
[H][C@@]1(O[C@@]([H])([C@H](C)[C@H](OC)C(C)=CC=CCNC(=O)[C@@H](CC)C2(O)OC(C=CC=C/C)C(C)(C)C(O)C2O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O)C=CC=CC=C(/C)C(=O)C1=C(O)C=CNC1=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in methanol or DMSO.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Streptomyces collinus.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. Store solutions at -20°C in the dark.
Documents
References
Metabolic products of microorganisms. 99. Kirromycin: H. Wolf & H. Z?hner; Arch. Mikrobiol. 83, 147 (1972) | Kirromycin, an inhibitor of the 30 S ribosomal subunits function: H. Wolf, et al.; FEBS Lett. 21, 347 (1972) | The total structure of the novel antibiotic mocimycin: C. Vos & P.E.J. Verwiel; Tetrahedron Lett. 1973, 5173 (1973) | Kirromycin, an inhibitor of the protein biosynthesis that acts on elongation factor Tu: H. Wolf, et al.; PNAS 71, 4910 (1974) | Mechanism of the inhibition of protein synthesis by kirromycin. Role of elongation factor Tu and ribosomes: H. Wolf, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem. 75, 67 (1977) | Action of pulvomycin and kirromycin on eukaryotic cells: B. Schmid, et al.; FEBS Lett. 96, 189 (1978) | Energetic aspects of the EF-Tu-dependent GTPase activity. A study using the antibiotic kirromycin: V. Bocchin, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem. 113, 53 (1980) | Effects of elfamycins on elongation factor Tu from Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus: C.C. Hall, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 33, 322 (1989) | Inhibitory mechanisms of antibiotics targeting elongation factor Tu: T. Hogg, et al.; Curr. Prot. Pept. Sci. 3, 121 (2002) | Elongation factor Tu-targeted antibiotics: four different structures, two mechanisms of action: A. Parmeggiani & P. Nissen; FEBS Lett. 580, 4576 (2006) (Review) | Molecular analysis of the kirromycin biosynthetic gene cluster: T. Weber, et al.; Chem. Biol. 15, 175 (2008) | GTPase activation of elongation factor EF-Tu by the ribosome during decoding: J.-C. Schuette, et al.; EMBO J. 28, 755 (2009) | Interaction of apicoplast-encoded elongation factor EF-Tu with nuclear-encoded EF-Ts mediates translation in the Plasmodium falciparum plastid: S. Biswas, et al.; Intern. J. Parasitol. 41, 417 (2011) | The phosphopantetheinyl transferase kirP activates the ACP and PCP domains of the kirromycin NRPS/ PKS of Streptomyces collinus T? 365: M. Pavlidou, et al.; FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 319, 26 (2011)